The source of rotation of the gas-plasma mix is not just the processes which are occurring in it, but also the firm kernel which rotates quicker than the gas-plasma mix.
In this case, it is necessary to create a physical-mathematical model of the processes of such complex rotation. If we consider the equatorial rotation of the gas-plasma mix as a result of the kernel rotation, than — the value of rotation speeds with increase of the radius is decreases, as shown in fig. № R-5.2.
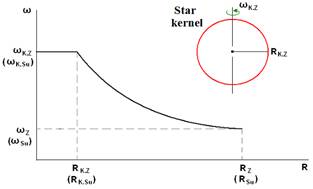
(86) Figure № R-5.2
With the movement of the rotation plane considered to the poles, the section of the kernel in point «A» decreases fig. № R-5.3 Hence, the speed of rotation on the star (Sun) surface will decrease as well.
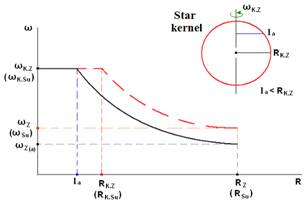
(87) Figure № R-5.3
Since the surface of the star in the section of point «A» is also suited under the action of the firm kernel, the change of speed on the surface should be smooth. Vortex rotation should be received on the rotation axis received from rotation of a kernel. This vertical rotation should be supported by the rotation of the kernel. In this case, changes of speeds should be more appreciable on the star surface. The speed decrease at the poles can be explained by the presence of vortex rotation in the center. Vortex rotation supposed to affect all of the gas-plasma mix. What influence the kernel rotation has on the processes in the gas-plasma mix?
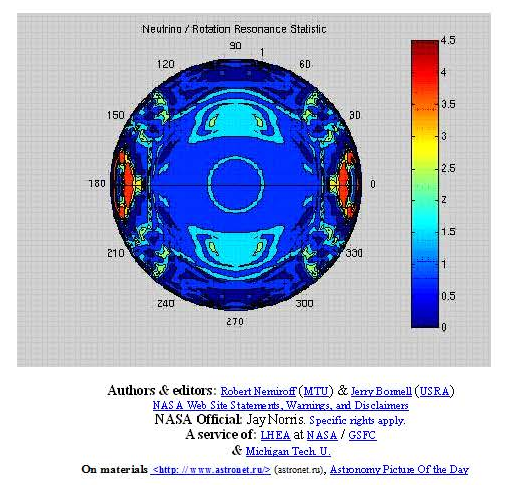
Certainly, such complex rotation should influence the processes occurring in a star. We shall consider the internal processes on the interzonal map of the Sun, which was based on neutrino radiation (figure № R-5.4).
(88) Figure № R-5.4
We shall see symmetry or a mirror image of the processes. It might be possible to explain this symmetry with the influence of rotations of a «firm» star kernel on the processes in the gas-plasma mix.
The star rotation influences the processes which are occurring in it, including the processes of synthesis of atom kernels, hashing of the substance, and thermal processes. The fast rotation of a kernel should create a vortex rotation in the internal star layers. The synthesis of kernels of atoms, both with allocation and with absorption of energy supposed to influence the star rotation. The influence on the synthesis and the star rotation should be created by other processes occurring in the star. At the present, the science cannot explain precisely the existing of difference in speeds between the kernel and other layers of the star. After the creation of physical-mathematical model, while considering thermal processes and synthesis processes, researchers will probably be able to establish a law of star rotation influence on the processes occurring in the star, and the influence of processes occurring in the star on the moment of its rotation.
3. Gravitation force of FG.
On a particle with weight mi the force of gravitation operates, directed to the star’s center. The equation for this force is complex, since this particle is inside the star, which is a source of a powerful gravitational field. The second reason which complicates the calculations is the different density of the star matter. During the star’s life, a firm kernel is formed in its central part — «the white dwarf», which is an additional source of gravitation.
The weight of a sphere:
![]()
Where R — the sphere radius,
ρ — the specific weight of a sphere.
The weight of a star can be defined by the formula:
![]() (5.11)
(5.11)
Rz — star radius
ρz — specific star weight.
For «the white dwarf» the weight is defined by the formula:
![]() (5.12)
(5.12)
Where RBK — the radius of «the white dwarf»;
ρBK — specific weight of «the white dwarf».
The weight of a star is consisted of weights, gas-plasma mix, «the white dwarf» and radiation,
MZ = MGP + MBK + MIz