(49)
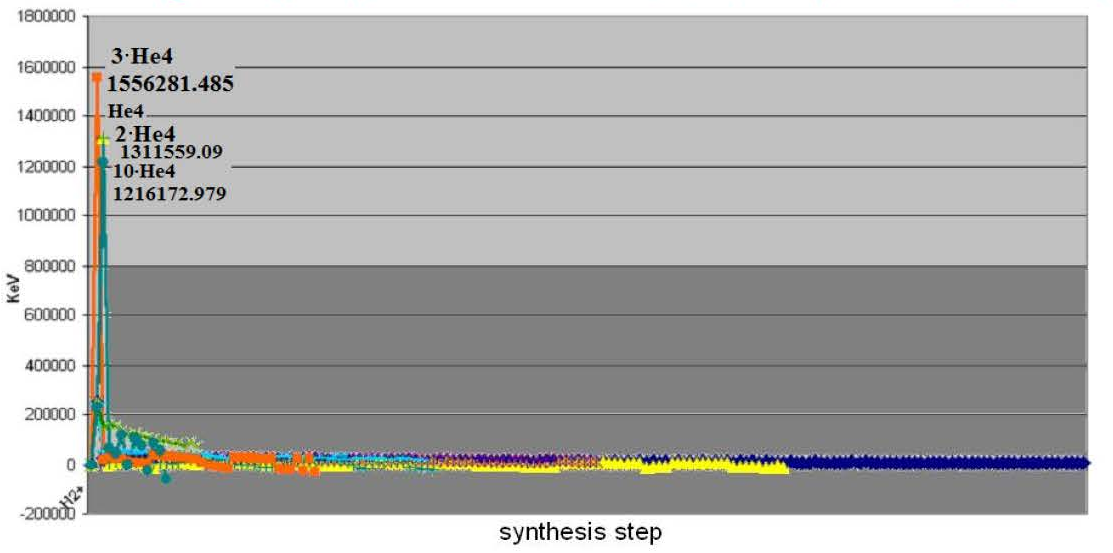
Allocation of energy during the synthesis: KERNEL + 1; 2; 3; 10 easy kernels (H-2, He-4).
(50) Schedule № G-3.7.
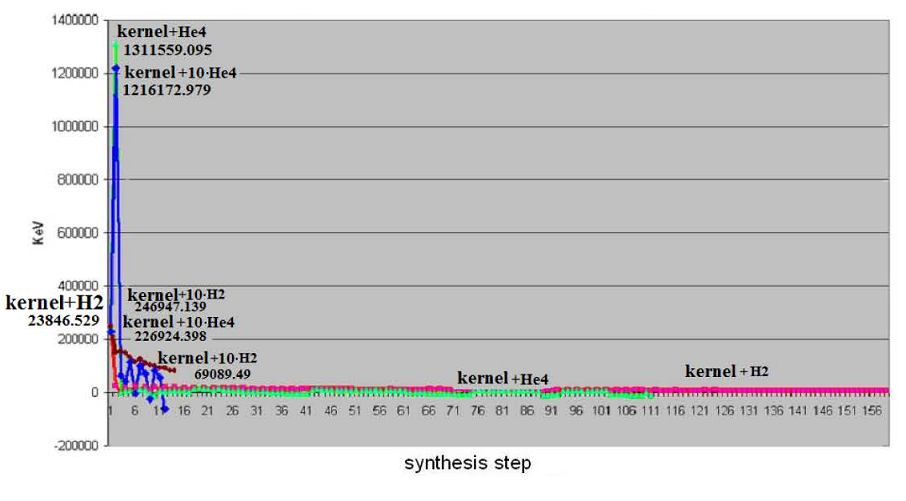
Allocation of energy during the synthesis: the KERNEL + 1 10 easy kernels (H-2, He-4).
(51) Schedule № G-3.8.
From calculations and the schedules constructed by them results it is visible, that the maximal allocation of energy occurs during the synthesis of easy kernels which concentrated in the top layers of a star, and it confirms the activity of nuclear processes in stars atmospheres (Sun).
— Conclusions:
— Most of the energy in stars is allocated during the synthesis of easy kernels which due to their small weight are located in higher layers of stars, than atoms of heavy elements and their kernels. Hence, most of the energy is allocated in the top layers.
— Probably, under the action of dynamic processes occurring in the top layers of an atmosphere, in the average or bottom layers of an atmosphere of a star areas of thermonuclear reaction of synthesis, easy kernels (nuclear explosions) are being formed. These areas of thermonuclear reaction of the synthesis, under the action of Archimedes force are rising in the top layers of the atmosphere and form a photosphere and chromospheres.
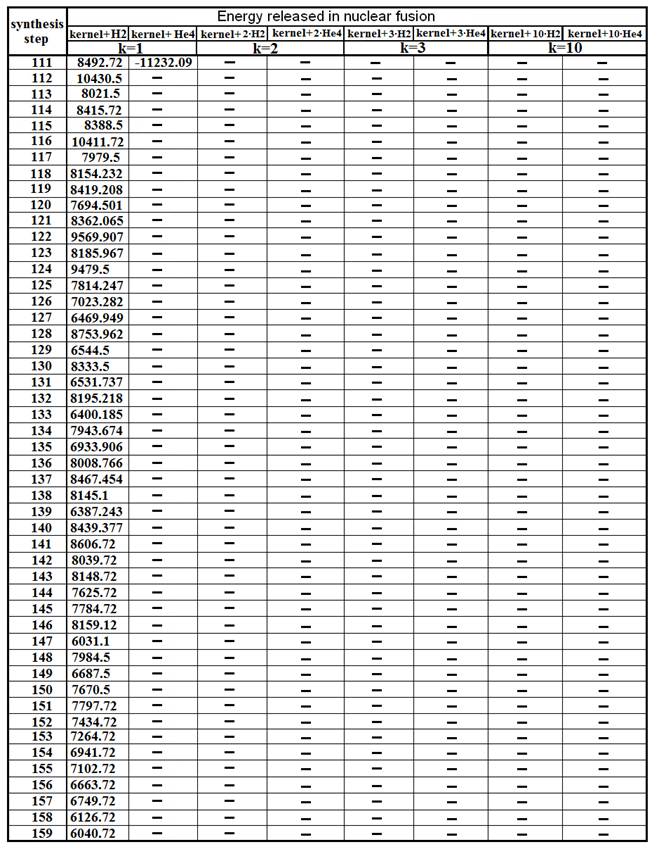
— With the increase in weight of kernels, the allocation of energy during the synthesis decreases, and during the synthesis heavy and over heavy kernels — the energy is being absorbed.
— The allocation of greater energy in the top layers compresses internal layers of a star and keeps the atmosphere in its volume.
— In the central part of a star, there are heavy kernels that under the pressure of compression by gravity gather and condense «the white dwarf». Probably, further synthesis of heavier kernels goes on the surface and inside «the white dwarf». In «the white dwarf», heavy kernels, atoms and molecules are being collected, and there are the reason of a collapse (explosion) after the «death» of a star.
— At moment of synthesis of kernels the energy is allocated in the different parties. Part of this energy is allocated and dissipates in space. Other part directed inside, raises the temperature, the pressure in the gas-plasma mix (creating conditions for synthesis of kernels), generates process of synthesis and absorbed during the synthesis of heavy kernels.
The part of energy allocated in inside stars, is absorbed by heavy kernels of atoms, and accumulated in «the white dwarf», forming and increasing its weight sizes. The quantity of heavy atoms in a kernel of star (in «the white dwarf») increases. In conditions of stars, these heavy kernels are natural accumulators of energy.
— Large allocation of energy during the synthesis of easy kernels, informs greater speed to these kernels, increasing their impulse. At the synthesis of heavier kernels, the allocation of energy is less, so is their speed and impulse; hence, the probability of synthesis of heavier kernels decreases. At heavy and over heavy kernels, during the synthesis, energy and weight are being absorbed, that reduces the probability of their synthesis among themselves to zero. But the probability of synthesis of heavy kernels under the influence of dynamic pressure from easier kernels (at their synthesis) exists. There is a probability of a synthesis between heavy kernels as well, due to dynamic compression of the substance to the center of a star, by the action principle of a hydrogen bomb.