The conclusions made by us by regarding the chain of synthesis of a kernel with Z=111, A=272 are also fair for the chain of synthesis of a kernel with Z=110, A=272 and for other variants.
Let’s consider the changes of allocation of energy, at the participation in one act of synthesis of over two kernels or nuclides as shown in schemes № S-3.7 and № S-3.8 — for three kernels;
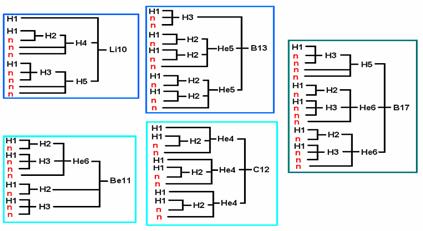
(31) Scheme № S-3.7
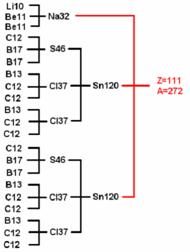
(32) Scheme № S-3.8
For four kernels — the scheme № S-3.9;
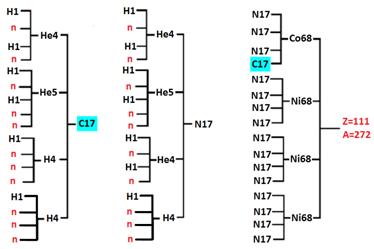
(33) Scheme № S-3.9
For ten kernels — the scheme № S-3.10.
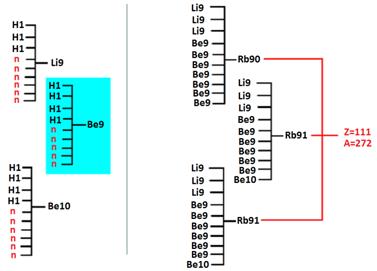
(34) Scheme № S-3.10
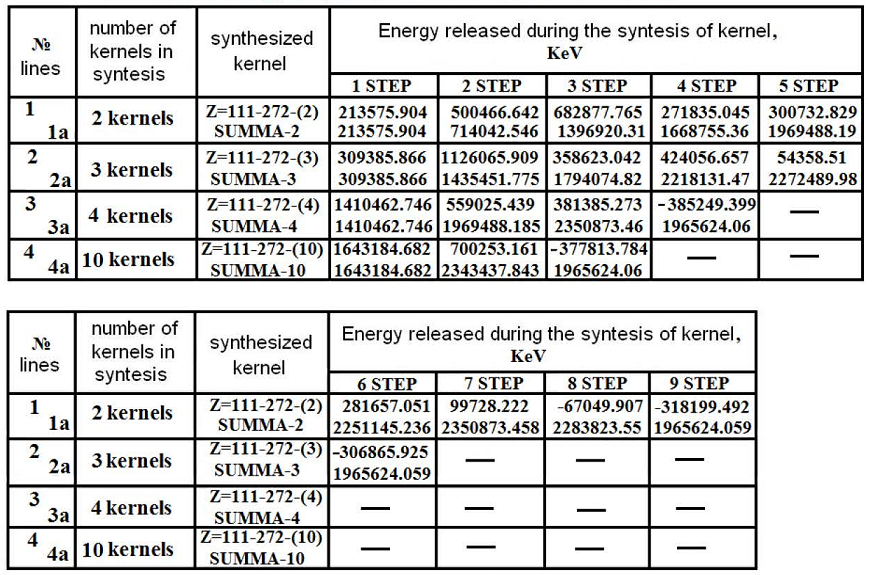
In the table № T-3.4 the results of calculations are yielded, allocation of energy, in time of synthesis of kernels on chains represented on schemes: № S-3.2, № S-3.3, № S-3.4, № S-3.7, №S-3.8, №S-3.9, № S-3.10.
(35) Table № T-3.4
Allocation of energy at synthesis of kernels with Z=111, A=272.
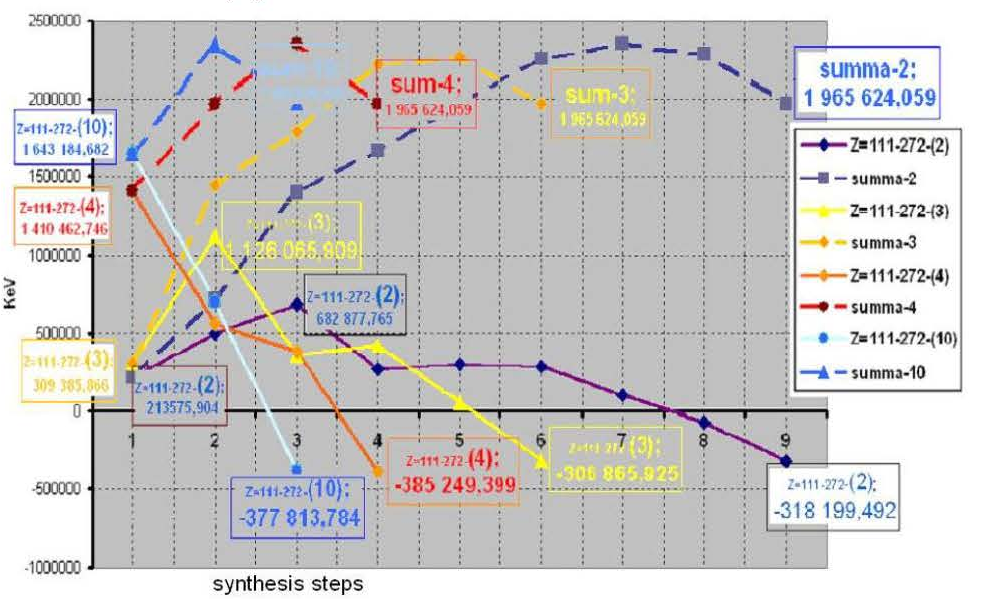
The schedule № G-3.4 is constructed under the table № T-3.4.
Allocation of energy in time of synthesis of a kernel with Z=111, A=272 by synthesis
2, 3, 4 and 10 kernels and nuclides.
(36) Schedule № G-3.4.
Apparently from the schedule № G-3.4 with increase in number of kernels and nuclides, participated in one act of synthesis, the quantity of steps of the synthesis is reduced, and allocated energy in each act and in each step increases, except for the last. A total sum of the allocated energy in all variants of synthesis is the same, although at each step its value increases with the growth of number of kernels in each act of synthesis. That means all energy allocated at the synthesis of a kernel with increase of number of kernels, participated in one act of synthesis does not change, but its allocation occurs for a smaller time interval.
The distribution of this energy on a chain of synthesis is uneven. Most of the allocated energy is necessary on the area of synthesis of easy kernels: hydrogen H, helium He and lithium Li. The increase in number of kernels and nuclides in one act of synthesis also does not change the distribution of allocated energy on a chain, but increases its value, especially in the field of easy kernels.
And since the easy kernels of atoms, due to their weight, are settling down in the top layers of a star, most of energy should be allocated in same higher layers. Such allocation of a most of the energy in the top layers should lead to compression of the central part of a star. At the increase of quantity of the kernels participated in one act of synthesis, the allocated energy in the top layers that increases compression of the central part increases. The maximum quantity of easy kernels contained in a star at the initial stage of its life, hence, there is also a maximal compression of its central areas during the same period. During the same period it is probable, there is the maximal participation of kernels and nuclides in one act of synthesis, which increases the allocation of energy in it, and reduces the time of life of a star. At decrease in stocks of hydrogen the quantity of acts of synthesis of easy kernels (H, He and Li), that decreases reduces allocation of energy in the top layers, reduces compression of the center of a star and reduces quantity of kernels and nuclides, participating in each act of synthesis, it leads to increase in time of a life of a star. Hence, it is not possible to calculate the life time of a star on a linear dependence.
In analytical work it is necessary to consider as much variants of succession of events as possible. Since most of energy is allocated during the synthesis of easy kernels, it is not difficult to guess, that the greatest speeds are distributed between these easy kernels, as the analysis of speeds of kernels participating in synthesis has confirmed.
Hence, the variant of synthesis, with the participation of one any «initial» kernel and one easy (H, He, Li…) is possible. The given variant is possible:
— As the basic, means, the synthesis in stars goes only this way;
— As the basic variant of the synthesis, only in stars with small weights;
— As the basic variant of the synthesis in stars in the end of life, when just the easy kernels contain enough allocated energy for the continuation of the synthesis.