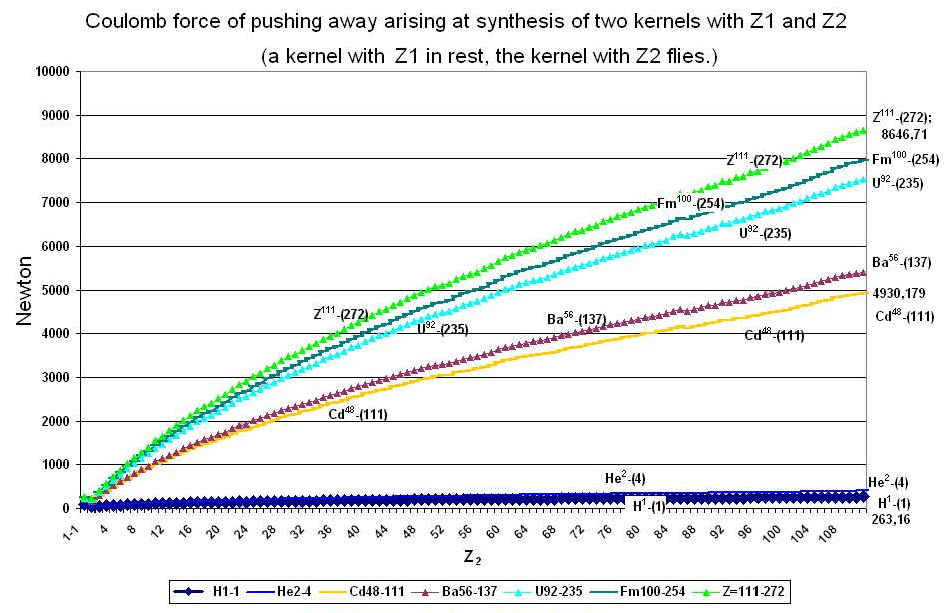
(25) Schedule № G-2.10
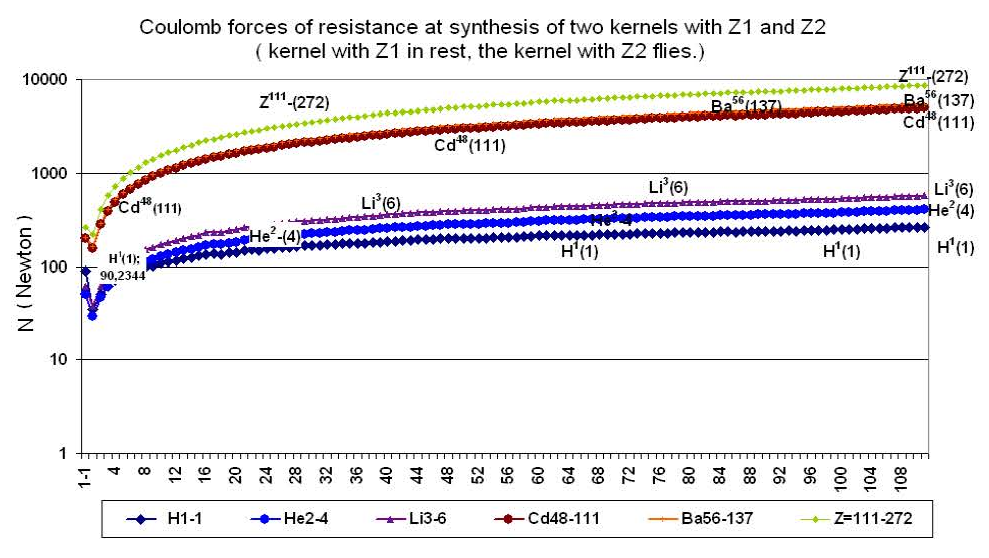
(26) Schedule № G-2.11
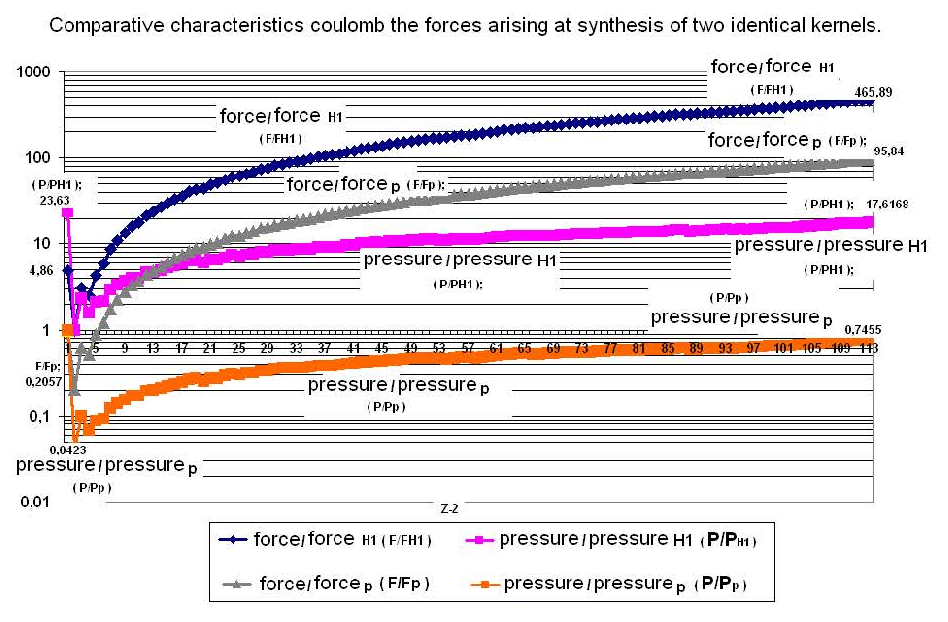
(27) Schedule № G-2.12
On schedules №G-2.10, №G-2.11, № G-2.12 the increase of coulomb forces of pushing away is shown at increase in a charge z2 and mass number А2 of a moving (flying) kernel.
As we see, the increase of coulomb forces with growth z2 goes almost under the linear law. For presentation, schedules № G-2.8, №G-2.11 and № G-2.12 are constructed with a logarithmic scale on an axis «Y».
As we see, from the schedules, the first point on each line characterizes the coulomb force created at the moment of synthesis of a kernel with a proton (or with a kernel of hydrogen with z2=1 and А2=1). The value of the force in these reactions is higher than at synthesis of the same kernel, but with kernel Н with z2=1 and А=2.
It may be explained by the radius at proton Rp=0.8 fm which is smaller, than at other kernels, and by the dependence of value of radius in other atoms kernels — Rj = 1.4 . Аj1/3 fm. The Increase of coulomb forces concerning the reaction ( +p++p) between reactions of synthesis between kernels increases up to:
— 0.89 and 1.2 times, for two kernels Li (with z=3 and А=6) and two kernels Be (with z=4 and А=9);
— 37.9 times, for two kernels Cs (with z=55 and А=133);
— 71.9 times, for two kernels U (with z=92 and А=238);
— 95.84 times, for two kernels with z=111 (the Schedule № G-2.12).
The further analysis we shall lead is not regarding the coulomb forces, but for the pressure which create these forces on the area of cross-section of kernels they are enclosed to. It is possible to consider the pressure which needed in order to create the coulomb forces as the minimal pressure which is necessary in order to create on the area of cross-section of a kernel, for overcoming coulomb forces of resistance, at the participation of the given kernel in synthesis.
Let’s disassemble, under which conditions there is a synthesis of kernels in a star:
— The heat — increasing kinetic energy of kernels of atoms and the influence on the internal parameters of a star.
— High static pressure — is created by the gravitational force due to the big weight of a star,
— influences the density of star’s substance, and parameters of magnetic and other fields.
— The high pressure created by dynamic processes and radiation, at thermonuclear synthesis in the top layers of a stars atmosphere, influences the dynamic compression of both the star, and its central areas, keeps the weight of the heated gas in the volume of a star, not giving this gas an opportunity to extend.
— The high density of substance in a star, especially in its central part, is created by both static and dynamic pressure.
Let’s consider a variant when two kernels participating in the synthesis. A kernel with z1 and А1 and the second kernel with z2 and А2.
For the synthesis of two kernels, the main necessary condition is their meeting, which will probably lead to a synthesis of these kernels. For a meeting of these kernels it is necessary, that one or both kernels moved to a point of their meeting.
We shall disassemble two possible cases:
1) the kernel with z1 and А1 — is motionless, and the kernel with z2 and А2 flies on the first.
2) Case when a kernel with z1 and А1 and a kernel with z2 and А2 move to a point of their meeting, and possibly leading to a synthesis.
Let’s analyze the dynamics of pressure change created by coulomb forces on kernels with z1and z2 in the two cases offered, under the condition of parameters change in zj and Аj of both kernels.
First case:
Kernel with z1 and А1 — was based v1=0
The kernel with z2 and А2 — flies on a kernel with z1, v2> 0.
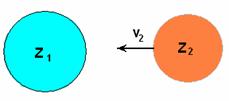
(28) Figure № R-2.13
In this case the pressure necessary for overcoming coulomb forces should be enclosed to a kernel two, with z2. Hence, the pressure is necessary to count regarding the area of cross-section of a kernel with z2 in the formula
p2=FQ/σ2 (2.97)
Where p2 – the pressure which is necessary in order to create synthesis in kernel with z2 for.
σ2 — the area of cross-section of kernel with z2.
Having substituted in the formula (2.97), the values for kernels, with different zj and Аj, by the calculations results have constructed schedules № G-2.13 and № G-2.14.
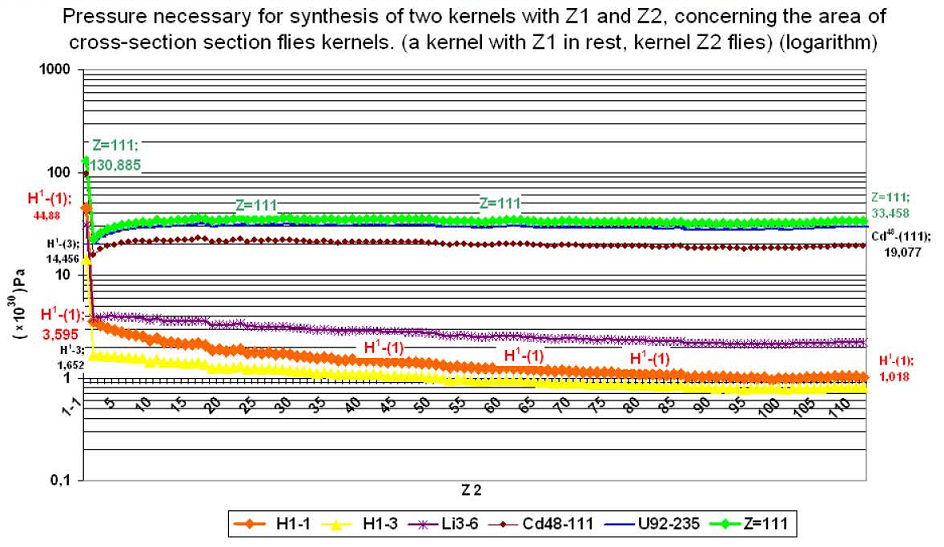
(29) Schedule № G-2.13
(30) Schedule № G-2.14
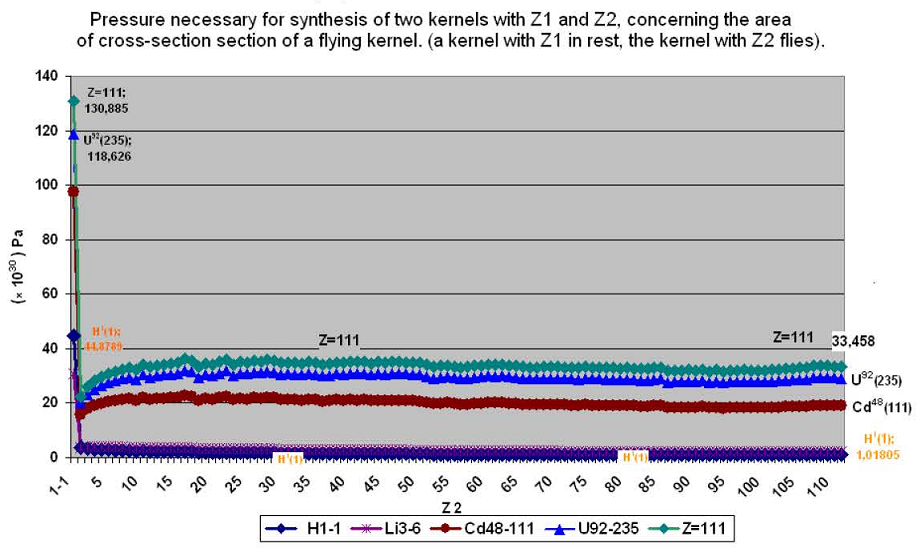
From the given schedules it is visible, that with the growth of zj and Аj both for a kernel №1 and for a kernel №2, the pressure which is necessary to create on a kernel №2, for overcoming coulomb forces, is not only does not increase with the increase of z2 and А2, and at some values z1 and А1 decreases with growth of value z2 and А2. Itischaracteristicforeasierkernelswithz1.
For kernels with z1 in the middle of the periodic table of elements (Mendeleyev table), the pressure which is necessary to render on a kernel with z2 for synthesis, is almost equal, on all the range of a scale z2, and lower the necessary value of pressure for rapprochement of two protons
p(р+р)=130.885 . 1030 Pa
So for example: for motionless kernel Cd with z1=48 and А1=111 the value of pressure p2 for flying kernels with z2 and А2 for hydrogen Н with z2=1, А2=2 — p2=15.73 . 1030 Pa;
For Cd with z2=48, А2=110 — p2=20.85 . 1030 Pa
For z=111 с z2=111 А2=272 — p2=19.077 . 1030 Pa.
From the given analysis it is possible to draw a conclusion, that with the increase of z and A flying kernel (z2) the necessary pressure is not only does not increase, as the coulomb force, but remains approximately at one level. In case of when the motionless kernel z1 concerns as easier, the pressure p2 decreases with increase of z2 and А2.