If there is an increase in pause time, and the time the signal is reduced or not changed, then this increasing in pause occurs at the expense of a radioactive substance of the «neutron star». This should decrease also the signal strength, although it’s difficult to fix decrease of power at large distances.
Over time, the radioactivity of the «neutron star» is reducing. Consequently, the power and time signals must also decrease, and the pauses to increase and these changes must occur according to an exponential (logarithmic) law.
Let’s return to the analysis of rotation of the neutron star. Illustration № R-9.11 shows the angle of «neutron stars» and the way of the point, emitting a signal on its surface.
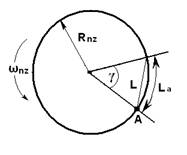
(164) Illustration №R-9.11
γ — angle of rotation of the «neutron star»;
А – the point that emits a signal that can be received on Earth;
La — the path passes by the point A on the surface of a «neutron star» during the time passages of signal;
Rnz – the radius of «neutron star»;
ωnz — the speed of rotation of the «neutron star».
The linear velocity of point А, on the surface of the «neutron star» is defined by the formula:
Va = ωnz. Rnz
La = Va . τa
where, τa — is receiving a signal from point A on the Earth.
From geometry we get
L = 2 . Rnz . Sin(γ/2)
La = 2 . π. Rnz . (γ/360) = 0.01745 . γ. Rnz
![]()
Consequently, in the time of signal and pause there are «encrypted» the speed and radius of the «neutron star».
The change of radioactivity gives us valuable information.
Since, the radioactive substance decreases more rapidly that the reducing of the rate of rotation of the «neutron star», some details of the «neutron star» can be determined by examining changes in the receiving of the signals, assuming that the rotational speed of the object has not changed.
Of course, it is necessary to explore the possibility of influence on the pulse of the superposition of signals on each other and focusing signals at a given point of the entire surface of the «neutron star». But the logarithmic decrease in the frequency of signals received from a «neutron star» announcing the reduction of radioactive material of the «neutron star». Hence, the reason for the high oscillation signal from the «Neutron Star» is not a high rate of rotation, but the reception of signals from adjacent sources of radioactivity, which, in large numbers are located on the entire surface of the «neutron star».
The separation of the signals is ongoing due to the large removal of the source signals from the Earth. Meanwhile, there is a dispersion of the total flow of signals from its expansion into separate signals.
How can we check the hypothesis we expressed? Very simple, it is necessary to create one or more space instruments, devices which will record the signals of the «neutron star». To synchronize watches, in the devices and on earth (at the research center).
To expand the space instruments to a great distances from each other, but placed on one level with the test object, and make to measurements. Also, to conduct similar studies of other similar objects. If the time of receiving a signal from the «pulsar» matches in two or more devices, then our hypothesis is correct. Since, one beam cannot be fixed in two points in space simultaneously.
The signal that coming to us from any space objects is actually the encrypted information. That means transmitted with the speed of light. The main task of the analyst is to decipher this information.
To decode this information, we must study the world around us, its laws of force, and to create devices that capable of recording and measuring the weak signals coming from space.
Is it possible to determine some of the parameters of a «neutron star» — a pulsar by character of radiation?
While we have vast and different distances from the pulsar (radiation sources), it is very difficult to determine the parameters of space objects. Judging by the intensity, the radiation power and change in these parameters over time, we may determine some approximate characteristics.
By the explosive power, «neutron star» may determine the mass of the «white dwarf», and remain mass of the «neutron star»:
Мbc = Мnz + М0
Where Мbc — the mass of the «white dwarf»;
Мnz — the mass of the «neutron star»;
М0 — the mass, ejected in the collapse of the «white dwarf».
By the reduction the radiation power we may determine the power of the explosion and to compare it with the visual data, and try to suggest what part of the mass was ejected into space. This analysis should be dealt with physics, physics — nuclear physicists and mathematicians. After comparing several tests on different physical parameters, the same space objects may define a part of the characteristics of these objects.
— Outbreaks of supernovae.
The main physical processes that accompanying the star at the end of its life.
At the end of its life, the star is going into a «red giant» state. Since the energy of nuclear synthesis is no longer able to restrain the heated gas-plasma mix, the star’s atmosphere expands and increases its size over many times. If nuclear synthesis in the upper layers have prevented the expansion of gas-plasma mix and kept it in the territory of the star, in the case of the «red giant» the synthesis has the opposite role. During heating from the inside, the gas-plasma mix, the maximum expanding velocity of particles is kept high. Perhaps, dynamic processes (flares, explosions…) occur on the surface of the «white dwarf», which accompanies nuclear reactions. Perhaps these dynamic processes have contributed to an increasing size of the «red giant», and the heating of its atmosphere.
After the cessation of the synthesis and cooling of the gas-plasma mix in the center of the former «red giant» remains the «white dwarf» — the kernel of the star, which was formed during her life.
After the maximum expansion and cooling of gas-plasma mix around the white dwarf, a low pressure area relative to the gas surrounding space is formed — a vacuum. Heliosphere, which surrounded the star and restrained gas flows from outer space, decreases and disappears with the decrease and disappearance of the stellar wind. At this level of vacuum in the center of which the «white dwarf» is placed, the cosmic gas and dust is being absorbed. If we set the parameters of the former star and gas density of the surrounding space, it may re-start the nuclear synthesis around the «white dwarf» or the «neutron star».
The beginning of the synthesis is the result of dynamic processes in the gas mixture. That means drawn in from outer space into the volume of vacuum around the «white dwarf». These star flares that can be observed in flares over the new stars of the second type. For certain parameters of the star and its surrounding gas it is possible that these processes are repeated outbreaks of the same star, which is observed in binary systems.

